SSH Demystified: A Beginner's Guide to Secure Shell Protocol
5 min to read
8/12/2024
SSH (Secure Shell) is a cryptographic protocol used for securely accessing and managing remote servers.It encrypts data, ensuring confidential communication over untrusted networks.
Introduction to SSH
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution.
SSH was created in 1995 by Tatu Ylönen, a researcher at Helsinki University of Technology in Finland. Ylönen developed SSH in response to a security breach where a password was intercepted over an unsecured network
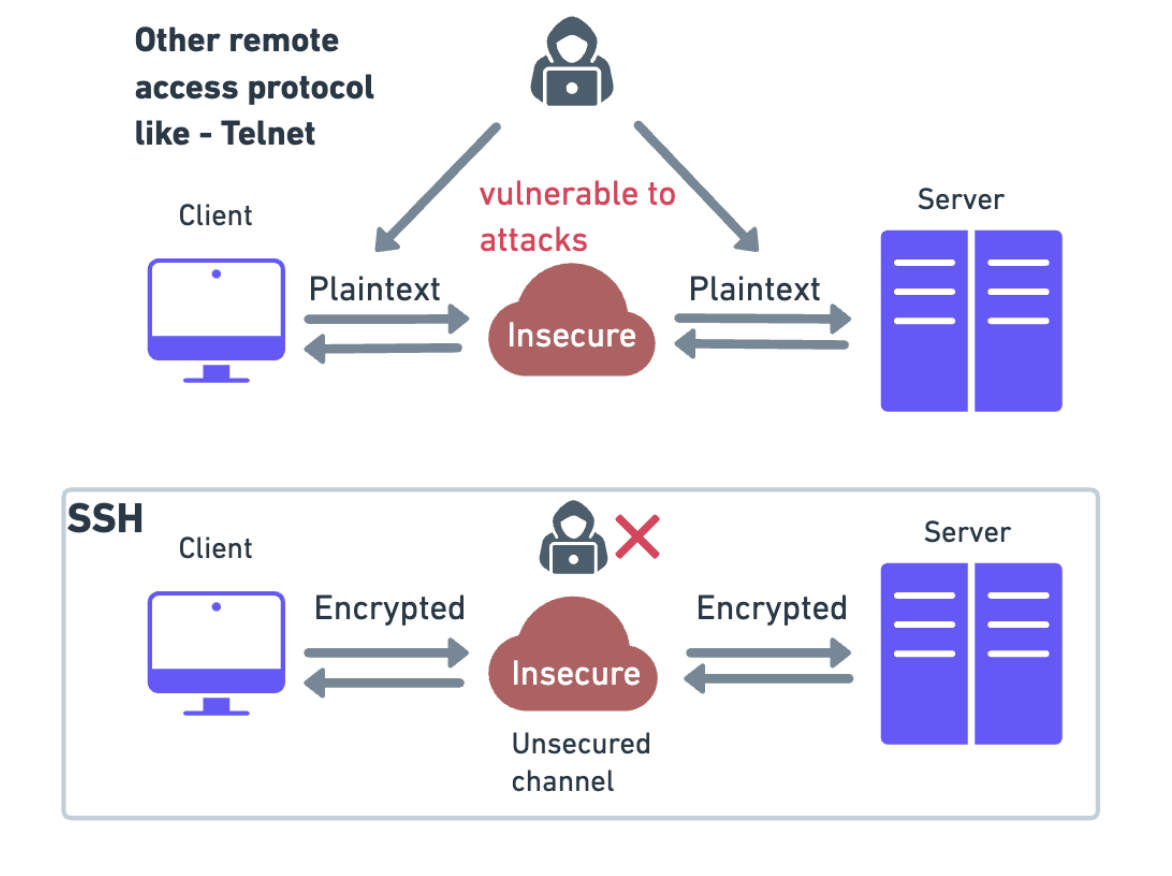
SSH was designed for Unix-like operating systems as a replacement for Telnet and unsecured remote Unix shell protocols, such as the Berkeley Remote Shell (rsh) and the related rlogin and rexec protocols, which all use insecure, plaintext methods of authentication, like passwords.
Overview
Before SSH, remote access protocols sent sensitive data unencrypted, making it vulnerable to attacks like packet sniffing. SSH introduced strong encryption to protect data in transit, enabling secure logins, file transfers, and system management over untrusted networks.
How SSH works
SSH is crucial for securely transmitting data over an insecure network, especially when you want to connect remotely to another computer. To establish a secure SSH connection, two components are required: an SSH client and an SSH server.
ssh client - This is the software or tool on your local computer that initiates the SSH connection. When you run the ssh command, the SSH client starts a process that handles the connection to the remote machine.
ssh server - This is the software running on the remote computer you want to connect to,these process listen all incoming ssh connection , once a connection established it handles authentication process, manage secure session etc.
Starting the SSH Client Process -
-
- When you run a command like ssh
user@remote_serverin your terminal, the operating system starts a process associated with the SSH client (ssh).
- When you run a command like ssh
-
- This SSH client process handles the connection to the remote server, including:
- Establishing a TCP connection.
- Performing the SSH key exchange and authentication.
- Encrypting and decrypting of data.
SSH server process -
-
- On the remote server, an SSH server process
(usually sshd)is always running, listening for incoming SSH connections.
- On the remote server, an SSH server process
-
- When your SSH client connects, the server-side process handles the authentication, manage session.
Steps in SSH
-
- TCP connection:- First the TCP connection is initiate and established between server and client,tcp provides a reliable, ordered and error-checked stream of data.
-
- Version negotiation:- Supported version , algorithm negotiation between an SSH client and server. Client tells server which version of ssh and encryption algorithm might be used and server responded with highest version and proper algorithm.
-
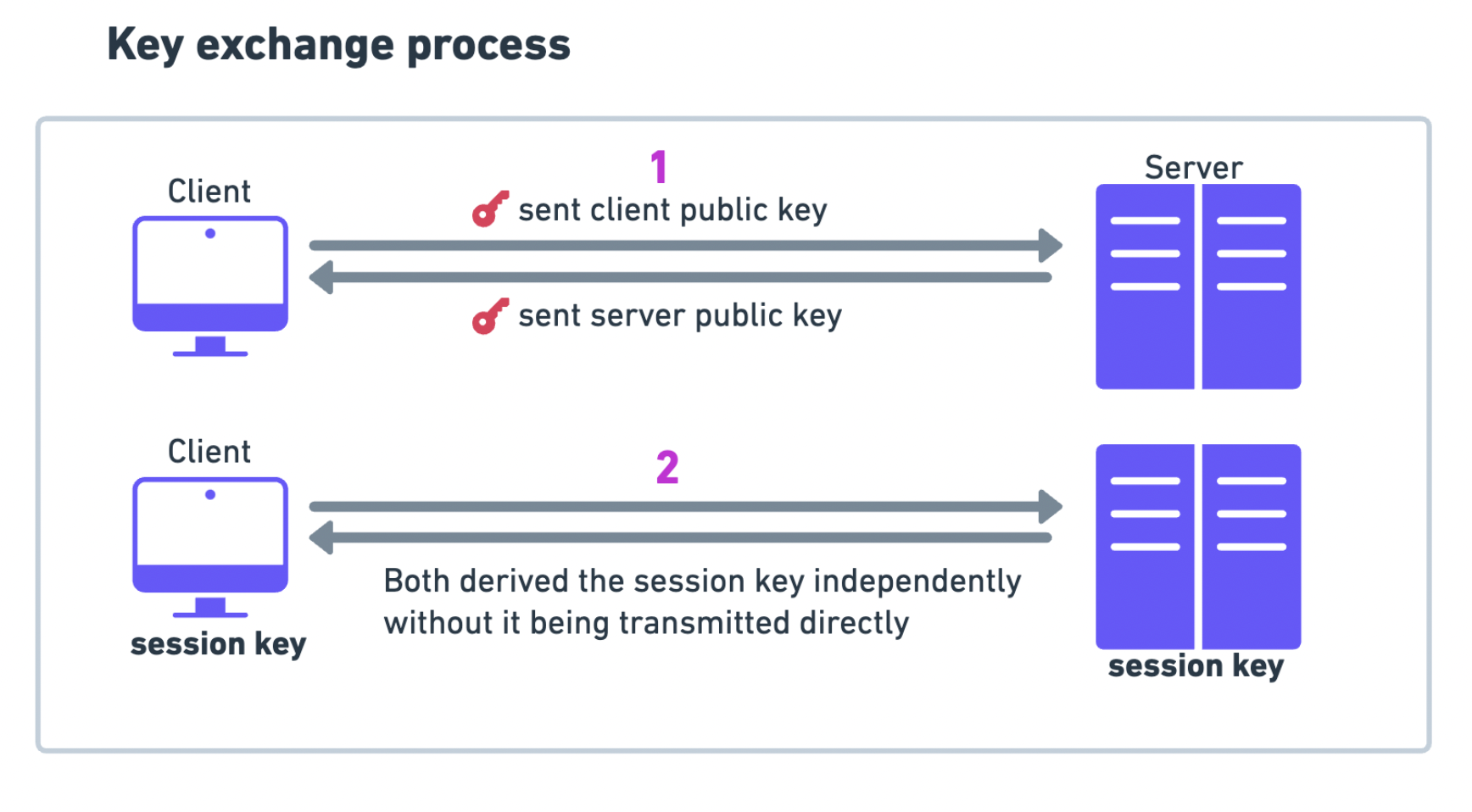
- Key exchange step -
- → Both parties agree on certain public parameters that will be used in the key exchange process.
- → Each party generates a private key. This key is kept secret and is not shared with anyone. The private key is a random number, and it plays a crucial role in the creation of the shared secret.
- → Using the agreed-upon public parameters (like p and g) and their respective private keys, each party calculates a public key. The public key is derived using a mathematical function
- → The two parties exchange their public keys. Since these keys are public, they can be transmitted over an insecure channel
- → Each party uses the other party's public key, along with their own private key, to compute a shared secret. The shared secret is then used as a symmetric key to encrypt and decrypt the data exchanged between the parties
-
4 . Server Authentication:- The server proves its identity to the client using its host key. The client checks the server's host key against a known list of trusted keys (usually stored in a file like
known_hosts). If the server's key is unknown or does not match, the client may prompt the user to verify it. -
5 . Client Authentication- in key exchange process both the parties have exchanged their public key.
- Public Key Sharing: → The client typically shares its public key with the server in previous step often by placing it in the server's
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile. - Challenge from Server: → When the client attempts to authenticate, the server challenges the client. It generates a random piece of data (a challenge) and sends it to the client.
- Client Signs the Challenge: → The client uses its private key to sign the challenge. This signed data is essentially the original challenge encrypted with the clients private key.
- Client Sends the Signed Challenge: → The client sends the signed challenge back to the server.
- Server Verifies the Signature: → The server uses the clients public key (which it already has) to decrypt the signed message.
- Public Key Sharing: → The client typically shares its public key with the server in previous step often by placing it in the server's
-
6 . Session Setup:- After successful authentication, an encrypted SSH session is established. The client and server agree on the use of symmetric encryption algorithms to secure all data transmitted during the session.
With the session fully established, the client and server can securely transmit data. This includes executing commands on the server, transferring files, or tunneling other network services through the SSH connection. The session continues until either the client or server decides to terminate it, at which point the TCP connection is closed.